The following sections outline the main hard- and software solutions on the market, including different SWOT analyses, evaluating their suitability to the aims of the project. The main hard- and software were evaluated with respect to their presence on the market, their various supporting media, the average purchase costs, hard- and software required, technical specifications, functionality, simplicity & handling and accessibility.
Table 3: Criteria Technical Evaluation of VR Hard- and Software
| Company | Device Name |
| URL | e.g.: https://www.samsung.com/uk/wearables/gear-vr-r324/ |
| Supporting Medium | e.g.: Smartphone, PC |
| Average purchase costs | e.g.: Online, Store |
| Software | e.g.: Android, IoS, System Requirements |
| Hardware requirements | e.g.: Phone, Minimum Version of phone |
| Technical specifications | e.g.: Resolution, Resolution per eye, Refresh rate |
| Functionality | e.g.: Tracking, Controller |
| Simplicity & Handling & Usability | e.g.: Plug & Play, Controller, Movements |
| Accessibility | e.g.: The scope of available software packages & available languages |
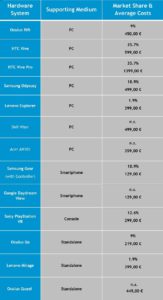
Below is a pre-defined selection of the 13 most popular devices that were chosen by the project group as suitable for further elaboration with respect to the main objectives of the SWOT analysis (cf. Annex I).
Table 4: Pre-Defined list of VR Hard- and Software[1]
For being able to better compare the different hardware systems, and further, to conduct a meaningful SWOT analysis of technologies (cf. Annex I, SWOT Analysis), three categories of hardware systems were defined prior to the technical elaboration. The categories and technical devices are:
PC-Based VR Devices
- Oculus Rift
- HTC Vive
- HTC Vive Pro
- Samsung Odyssey
- Lenovo Explorer
- Dell Visor
- Acer AH 101
Smartphone-Based VR Devices
- Samsung Gear
- Google Daydream
Stand-alone & other Devices
- Oculus Go
- Lenovo Mirage
- Oculus Quest
1.1 PC-Based VR Devices
According to the various technical elaborations of PC-based VR devices general commonalities, differences, advantages and disadvantages do exist (cf. Annex I). In comparison to the other devices, the HTC Vive and the HTC Vive Pro are the most expensive solutions. However, in terms of quality, performance, functionality and simplicity both devices offer outstanding capabilities. The average purchase costs for the Oculus Rift are reasonably low; however, in terms of performance, hardware requirements and functionality the device does not offer evenly high standards like the HTC solutions. Yet, it is proposed that the Oculus Rift offers a better price – performance – ratio. Both, the HTC systems as well as the Oculus Rift can be used on various VR software environments such as Windows, MacOs and Linux. Instead, Dell, with their Visor solution, the Lenovo Explorer, the Samsung Odyssey and the Acer AH 101 are based on Windows Mixed Reality software. Devices using Windows Mixed Reality software are, according to industry experts, easier to set. Yet, in terms of overall performance Windows based solutions are suggested to be in an inferior position to all other manufacturers. In comparison to smartphone-based and stand-alone solutions a major disadvantage of all PC-based VR solutions is, that they require more unoccupied space to fully function and that, in some cases, expensive external hardware (e.g. Computer) is needed.
The following SWOT analysis provides an overview on general strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of PC-based VR solutions.
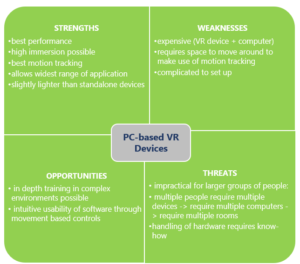
Figure 2: SWOT PC-Based VR DEVICES
1.2 Smartphone-Based VR DEVICES
With reference to the technical elaborations of the project partners the Samsung gear currently offers best performance amongst smartphone-based VR devices. Although Google’s cardboard solutions offer a wide range of possible applications, it is, in technical terms, not an actual VR device, but more an enhancing gimmick that enables phones to give a VR-like experience. The Google Daydream View database is rather small in comparison to the Cardboard database. Yet, it offers a steady performance. In comparison to pc-based VR devices, smartphone solutions’ major advantage is the ability to use and experience VR services anywhere at any time. Additionally, assuming a smartphone is already available, smartphone solutions are comparatively cheap by contrast with pc-based and stand-alone solutions. The following SWOT analysis provides and overview of smartphone-based VR solutions.
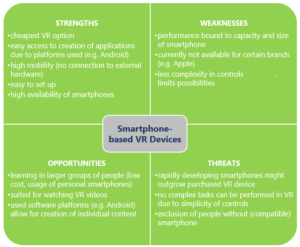
Figure 3: SWOT Smartphone-Based VR DEVICES
1.3 Stand-alone VR DEVICES
The focus of systems such as the HTC Vive, the HTC Vive Pro or the Lenovo Mirage is currently on gaming and entertainment, rather than applications in the educational sector. Yet, although stand-alone solutions presently have a relatively low presence on the market for VR devices, they are suggested to be well priced in comparison to pc-based solutions, especially, because further expensive hardware costs (e.g. for a pc) do not occur. The stand-alone devices Lenovo Mirage with Daydream and the HTC Vive Pro have further improved processing power while they are high in mobility. The following SWOT analysis illustrates the main aspects for stand-alone VR solutions.
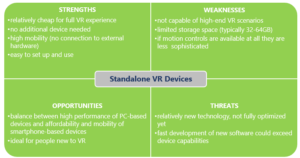
Figure 4: SWOT stand-alone VR DEVICES
BACK TO VR DIGEST OVERVIEW
[1] Average purchase costs as per December 2018.